Moving from Google Drive
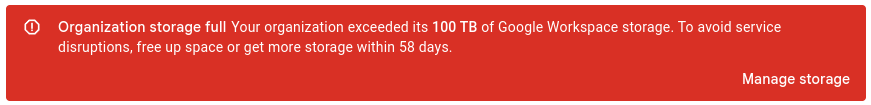
This morning, February 22, 2023, I opened up my Google Account here with YWM Kona and was treated with this announcement.
As a Google Reseller, I had seen this issue on some of my paid accounts and knew I needed to help update my customers.
But I had not seen this for a Google For Education account.
The short of it is that we are only allowed 100 TB of storage (Google Drive and Gmail combined), and we are way over this. We will need to do some purging and see how we can help departments that have been using this feature totheir advantage but now would have to pay for it.
Google pricing is $300 / month/groups of 10 TB.
What are the options?
I have customers that are using ReadyNAS and Synology. Personally, I like Synology.
This is a hardware device with between 4 and 12 hard drives in it. If you put 20TB Hard Drives in them you could have 80TB of storage, up to 240TB of storage.

rack Hardware
This NAS would be placed in a climite controlled server room.
RS3618xs
- It can hold twelve hard drives and comes with none.
- Six 1Gb ethernet ports.
- 8GB RAM
- Dual power supplies
- Install 12 x 16TB Drives
- Or create a set of Arrys.
- Can be expanded.
- Aproximitly $2,800
RS4021xs+
- Comes with 16 bays
- Approximmitly $5,812

hard drives
Always use recommended hard drives from Synology.
DS923 raid5
Seagate 16TB HDD Exos X16 – $269
$599 + $1,076 = $1,675
For 48TB storage. $35 per TB
DS1612+ raid5
Seagate 16TB HDD Exos X16 – $269
$965 + $1,614 = $2,579
For 80TB storage. $32 per TB
RS3618xs raid6
Seagate 16TB HDD Exos X16 – $269
$2,800 + $3,228 = $6,028
For 160TB storage. $37 per TB
RS4021xs+ raid6
Seagate 16TB HDD Exos X16 – $269
$5,812 + $4,304 = $10,116
For 224TB storage. $45 per TB

RAID 1
RAID 1, also known as “mirroring,” is a type of data storage technology that involves duplicating data on two or more hard drives. In a RAID 1 array, data is written to one hard drive and then mirrored, or copied, to the other drive(s), creating an exact duplicate.
RAID 1 offers several benefits, including increased data redundancy and improved data reliability. If one drive fails, the other drive(s) can continue to function, and no data is lost. This makes RAID 1 a popular choice for critical systems where data loss can have severe consequences.
However, RAID 1 also has some drawbacks. Since all data is duplicated on every drive, the total storage capacity of the array is limited to the size of a single drive. Additionally, RAID 1 does not provide any performance benefits compared to using a single drive.
Overall, RAID 1 is a straightforward and reliable way to increase data redundancy and protect against data loss.

RAID 5
RAID 5 is a type of data storage technology that uses a combination of striping and parity to protect against data loss. In a RAID 5 array, data is divided into blocks and written across multiple hard drives. One of the drives is reserved for parity information, which allows the array to recover data in the event of a drive failure.
Unlike RAID 1, RAID 5 offers both data redundancy and increased storage capacity. By striping data across multiple drives, the array can provide faster data access and improved performance compared to a single drive.
In a RAID 5 array with n drives, the total storage capacity of the array is (n-1) times the size of the smallest drive. For example, a RAID 5 array with three 1TB drives would have a total capacity of 2TB.
If one drive in a RAID 5 array fails, the array can continue to function in a degraded state. Data can be reconstructed using the parity information stored on the remaining drives. However, if a second drive fails before the first one is replaced and rebuilt, the data on the array can be lost.
Overall, RAID 5 is a popular choice for servers and other systems that require both performance and data redundancy. However, it is important to note that RAID 5 is not as fault-tolerant as other RAID configurations, such as RAID 6 or RAID 10, which offer more redundancy and protection against multiple drive failures.

RAID 6
RAID 6 is a type of data storage technology that provides increased data redundancy and protection against data loss compared to RAID 5. Like RAID 5, RAID 6 uses a combination of striping and parity to protect data.
In a RAID 6 array, data is divided into blocks and written across multiple hard drives. Two drives are reserved for parity information, which provides redundancy and allows the array to recover data in the event of up to two simultaneous drive failures. This means that a RAID 6 array can continue to function even if two drives fail, which is not possible with RAID 5.
Like RAID 5, RAID 6 offers improved performance compared to a single drive by striping data across multiple drives. In a RAID 6 array with n drives, the total storage capacity is (n-2) times the size of the smallest drive. For example, a RAID 6 array with four 1TB drives would have a total capacity of 2TB.
One potential drawback of RAID 6 is that it requires more processing power and additional storage for the parity information, which can lead to slower write performance and higher cost compared to RAID 5.
Overall, RAID 6 is a popular choice for systems that require high data redundancy and protection against multiple drive failures, such as enterprise-level storage systems or critical data applications.
Google as a Paid Service
With changes from Google you may be looking for a place for your data.
To help with this we are looking at offering services to meet this unfortunit new need.
Why is this happening?
Google has been saying for a while that all their unlimited accounts will no longer be unlimited.
This is them finally setting the price.
Every 10TB over their limit is going to cost $300 a month.
How do I get my files?
First, go to your Drive and delete what is not needed.
Do the same to your emails.
Log in to your campus account.
Follow this link.
https://takeout.google.com/
Choose what you want to download.
Wait for an email saying your download is ready Go back and download the zip files to a storage device.
I've got a question.
Can I buy data for my gmail account?
Yes, you can buy data for your gmail.com account.
Login to your Gmail account and follow this link.
https://one.google.com/about/plans
The 2TB account costs $12.00 a month.
How come I am using so much?
Go to Google Drive, and on the bottom left, click on the cloud Icon.
This will then show you your largest files.
Generally, your largest files will be videos and zip files, followed by photos.
What do your needs look like?
These accounts can be shared across several devices; my wife and I share one, so all our photos end up in the same place.
As a google reseller, I can offer you the same price and you get me to help technically.

Business Standard
- $12.00 / Month
- Custom and secure business email
- 150 participant video meetings + recording
- 2 TB storage per user*
- Security and management controls
- Support with ainet.biz (me)

Business Plus
- $18.00 / Month
- Custom and secure business email + eDiscovery, retention
- 500 participant video meetings + recording, attendance tracking
- 5 TB storage per user*
- Enhanced security and management controls, including Vault and advanced endpoint management
- Support with ainet.biz (me)

Enterprise Plus
- There is the possibility for accounts needing 10 to 100TB, I have a call in to Google on that for a price.
- Support with ainet.biz (me)

